Safety & Well-being
Login Tools
My Human Resources
Enter direct banking information, view earnings statements, change your address & manage training. [ LOGIN]
Pension Account
View pension plan balances and investment mix and choose your investments. [ LOGIN]
Manulife
Check and submit claims, get forms, print Manulife card. [ LOGIN]
Faculty Staff Resources
Salary ranges, pay schedules and related information. [ LOGIN]
Researcher Toolbox
Hiring/appointing research roles, including budgeting for salary and benefit costs. [ LOGIN]
Administrator Toolbox
Appointments and pay administration, offer templates. [ LOGIN]
Leader Toolbox
Help with recruiting, hiring, enhancing performance. [ LOGIN]
Western Financial
Submit expenses, PER inquiry, research grants. [ LOGIN]
Types of Nuclear Radiation
|
1) Alpha
|
3) Gamma and X-ray
|
|
2) Beta
|
4) Neutron
|
Radioactivity
- The rate of decay or transformation of a nuclear substance is described by its activity
- Curie (Ci) or becquerel (Bq) is a unit of measure for radioactivity
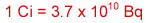
Physical Half-Life
- The amount of time required for an initial activity of a nuclear substance to be reduced by one-half or fifty percent (50%)
- Here are some common nuclear substances...
| Nuclear Substance | Types of Radiation | Half-life | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iodine 131 | Beta and Gamma medium energy | 8 days | Medical research & hyperthyroid treatment |
| Phosphorus 32 | Beta (high energy) | 14 days | Medical research |
| Iodine 125 | Gamma (low energy) | 60 days | Medical research |
| Sodium 22 | Beta and Gamma (high energy) |
2.6 years | Physics research |
| Tritium (H-3) | Beta (very low energy) | 12.3 years | Medical research |
| Americium 241 | Alpha (high energy) | 433 years | Smoke detectors |
| Carbon 14 | Beta (low energy) | 5,730 years | Medical research |
Published on and maintained in Cascade CMS.
